Introduced in March 2024 as an amendment to the REITs regulations of 2014, SM REITs lay out the regulations for investors, merchant bankers, trustees, investment managers to regulate fractional ownership as an investment structure.
In recent years real estate as an investment asset has remained inaccessible to the retail investor with high cost entry barriers. Nevertheless, with the advent of fractional ownership platforms, a lower entry barrier has been provided with technologically advanced management services and certified grade-A commercial and residential projects attracting the retail investor to venture into real estate and consequently diversify their investment portfolio. With the assets under management at these platforms reaching in the thousands of crores, SEBI deemed it necessary to be regulated.
The REITs regulations, introduced in 2014, were finally amended on March 8, 2024 to include SM REITs (Small and medium REITs) and laid out a comprehensive set of guidelines containing eligibility criteria, applicability, and regulations for investment managers, trustees, merchant bankers to best protect retail investors.
Explore this article to find out more about SM REITS.
Contents:
- What are SM REITs?
- Investment Manager’s Responsibilities
- Merchant Bankers Obligations
- Trustee’s Responsibilities
- SM REIT Investment Benefits for the Unit Holder/Investor
- Potential Risks in Investing in SM REIT
- Difference between Fractional Ownership and SM REITs
- Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are SM REITs (Small and Medium REITs)?
SM REITs (Small and Medium REITs) are a category of Real Estate Investment Trusts designed specifically to cater to smaller and medium-sized real estate portfolios. The regulations for SM REITs, outlined by SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India), are aimed at creating a structured environment for the operation and investment in these types of REITs. This overview will cover the regulations concerning the trustee, investor, and unit holders (investors) highlighting their roles, requirements, and benefits.
In a rapidly evolving real estate landscape, SM REITs have emerged as a crucial vehicle for fractional ownership. By pooling funds from multiple investors to purchase and manage real estate assets worth anywhere between INR 50 – 500 crores, SM REITs further democratise property investment.
To prioritise investor protection, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has taken significant steps through the 2024 amendments to ensure that SM REITs operate in an investor-centric manner.
These amendments introduce a comprehensive framework that places investor protection at the forefront. By clearly defining the roles and responsibilities of all the parties involved, SEBI ensures that investors’ interests are safeguarded throughout the investment lifecycle.
2. Investment Manager’s Responsibilities
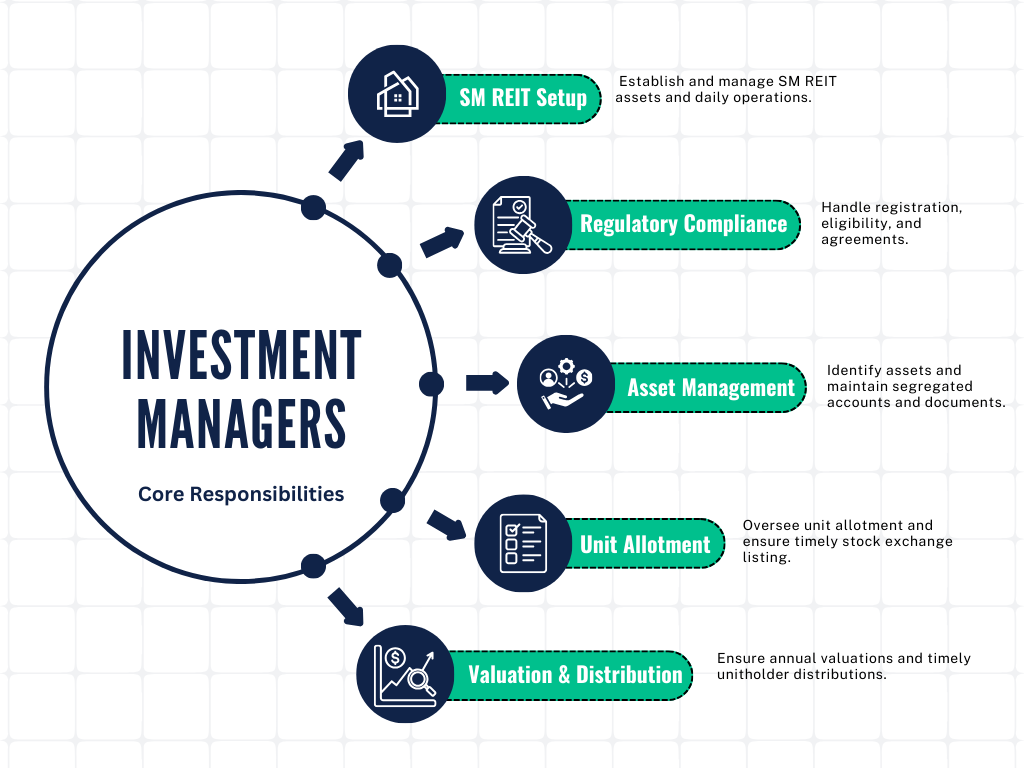
As per the regulations, investment manager means a company incorporated in India which sets up the SM REIT and manages assets and investments of the SM REITs.
The regulations go on to outline key responsibilities to ensure investment managers remain accountable for the smooth operation of essential functions within SM REITs.
Here is an overview of all of their obligations to the investor under the SM REITs regulations :
i. Setting up and managing SM REIT: The investment manager, on behalf of the trust, is tasked with establishing the SM REIT and overseeing its assets and investments.
ii. Operational Activities: The investment manager is responsible for the day-to-day operations of the SM REIT.
iii. Registration Application: The investment manager must apply for the SM REIT’s registration certificate on behalf of the trust.
iv. Compliance with Eligibility Criteria:
- Net Worth: Maintain a minimum net worth of INR 20 crores, with at least INR 10 crores in positive liquid assets.
- Experience: Either the investment manager or their key managerial personnel must have at least two years of experience in real estate or real estate fund management, or five years in these fields.
- Independent Directors: At least 50% of the directors must be independent and not serve on another REIT or SM REIT.
- Investment Management Agreement: Enter into an agreement with the trustee outlining the investment manager’s responsibilities.
v. Asset Identification and Management:
- Identification: Specify the real estate assets or properties for acquisition in the draft scheme offer document.
- Segregation: Ensure assets, bank accounts, investment or demat accounts, and books of accounts are segregated and ring-fenced for each scheme.
vi. Maintenance of Property Documents: Keep property documents and related papers in safe-deposit boxes at a scheduled commercial bank, with annual inspections by the trustee.
vii. Public Disclosure of Draft Scheme Offer Document: Make the draft scheme offer document available for public comment by hosting it on the Board’s, stock exchanges’, and associated merchant bankers’ websites for at least 21 days.
viii. Allotment Procedure and Basis of Allotment
- Allotment of Units: The investment manager is responsible for allotting units to applicants after receiving the application sum. This allotment is done on behalf of the scheme of the SM REIT.
- Ensuring Fairness in Allotment: Alongside authorised representatives of the designated stock exchange, post-issue merchant bankers, and registrars, the investment manager must ensure that the allotment process is fair and proper.
ix. Allotment and Listing of Units
- Mandatory Listing: The investment manager must ensure that the units of the SM REIT scheme are mandatorily listed on recognised stock exchanges with nationwide trading terminals.
- Timeline Adherence: The units must be allotted and listed within specified timelines. If the investment manager fails to meet these deadlines, they are required to pay 15% interest per annum to investors. This interest cannot be recovered as fees or in any other form payable by the SM REIT.
- Compliance with Listing Agreement: The investment manager must ensure that the listing of units complies with the listing agreement between the SM REIT and the designated stock exchange.
x. Delisting of Units
- Application for Delisting: The investment manager is responsible for applying for delisting of units if certain conditions are met, such as when public unit holding falls below the required limits, no assets remain in the scheme, or other regulatory violations occur.
- Redemption of Units: In case of delisting, the investment manager must sell the assets of the scheme to redeem units for unitholders and wind up the scheme as per the Board’s specifications.
xi. Valuation of Assets
- Annual Valuation: The investment manager must ensure that a valuer conducts a full comprehensive valuation of the scheme’s assets annually and submits the report within two months of the financial year-end.
- Material Developments: In the event of material developments affecting asset valuation, the investment manager must require a new valuation within two months.
- Independence of Valuer: The investment manager must ensure that the valuer is not an associate of the investment manager or trustee and that the valuer has the requisite qualifications and experience.
- Submission and Disclosure: The investment manager must submit the valuation reports to the trustee, designated stock exchanges, and unitholders within one working day of receipt and ensure timely disclosure of the net asset value.
xii. Distributions
- Distribution to Unitholders: The investment manager must ensure that 100% of the net distributable cash flows of the scheme are distributed to the unitholders and that distributions are declared at least once every quarter.
- Timely Payments: Distributions must be paid within seven working days of declaration. If delayed, the investment manager must pay 15% interest per annum to unitholders.
xii. Prohibition on Related Party Transactions: The investment manager must ensure that the SM REIT does not enter into any transactions with related parties, except for payment of fees to the investment manager and trustee for REIT activities.
xiv. Oversight of Meetings: The investment manager is responsible for all activities related to unitholders’ meetings, including ensuring that resolutions requiring approval are properly passed and that unitholders’ rights are protected. The investment managers are subject to oversight by the trustee
xv. Appointment of Merchant Bankers: The investment manager must appoint one or more merchant bankers registered with the Board to manage obligations related to the issue.
3. Merchant Bankers’ Responsibilities and Obligations
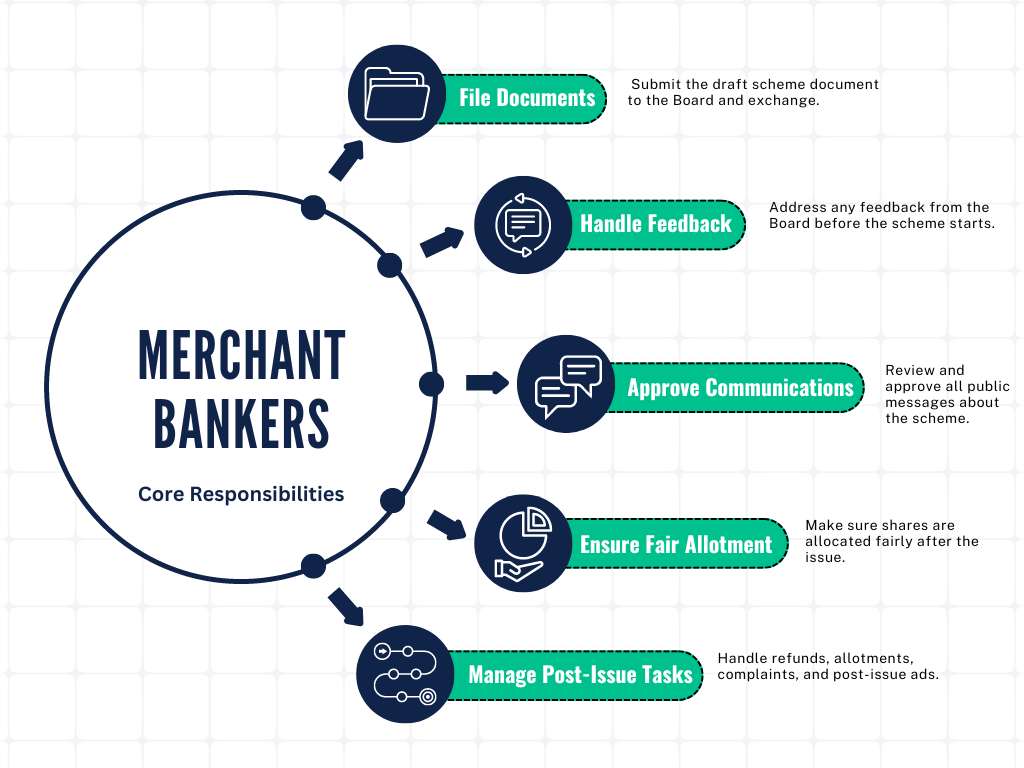
A merchant banker is a financial intermediary registered with the Board, responsible for managing various aspects of the issue process related to SM REITs (Small and Medium-sized Real Estate Investment Trusts). Their primary duties include:
i. Draft Scheme Filing: The investment manager appoints merchant bankers to file the draft scheme offer document with the Board and the designated stock exchange. This document outlines the details of the SM REIT scheme.
ii. Addressing Observations: The merchant banker must address any observations or comments from the Board on the draft scheme offer document before the scheme’s launch.
iii. Public Communications Approval: Any public communications about the SM REIT scheme must be approved by the merchant bankers responsible for marketing the issue.
iv. Fair Allotment Process: Post-issue, merchant bankers, along with stock exchange representatives, ensure that the allocation of shares is done fairly. They maintain a final book of demand showing the allocation results and cooperate with inspections of the book-building process.
v. Post-Issue Responsibilities: Post-issue, merchant bankers manage activities such as refunds, allotments, and investor grievances. They must also release advertisements related to the issue’s oversubscription, allotment details, and other relevant information within specified timelines. They ensure that no misleading statements about the issue’s response are made while it is still open for subscription.
4. Trustee’s Responsibilities
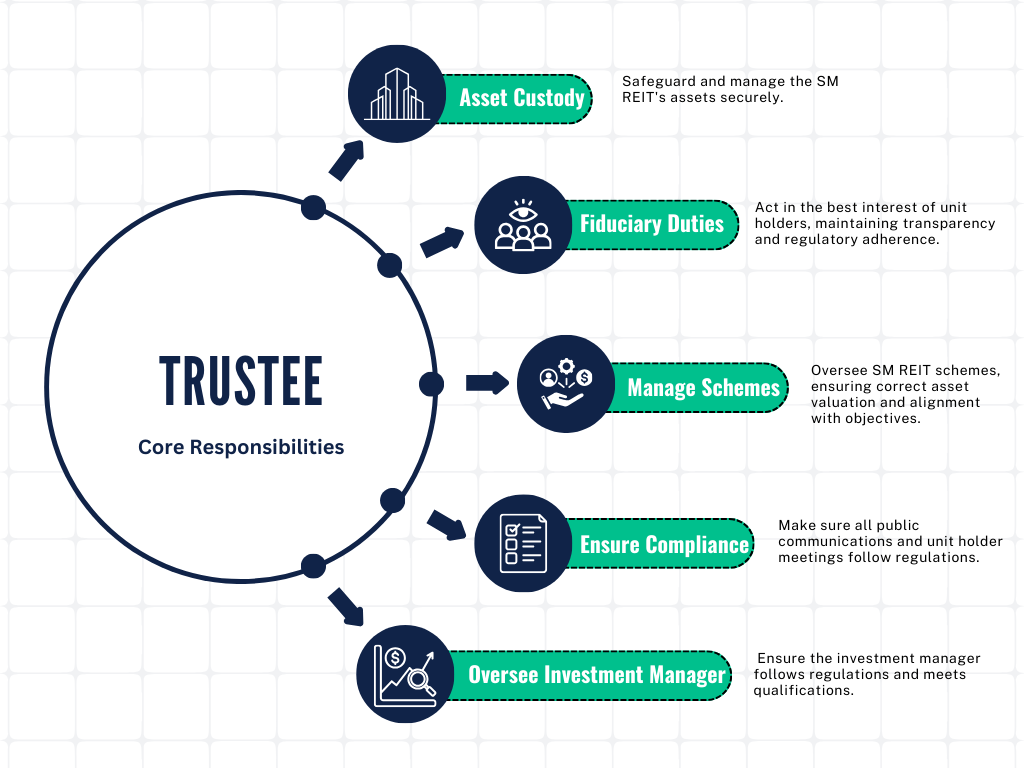
A trustee refers to a trustee registered with SEBI under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Debenture Trustees) Regulations, 1993. The trustee holds the assets of the SM REIT and its schemes in trust for the benefit of the unit holders, ensuring compliance with the regulations.
Under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Real Estate Investment Trusts) (Amendment) Regulations, 2024, a trustee in the context of SM REITs is defined and tasked with several crucial responsibilities:
i. Asset Custodianship:
- The trustee is responsible for holding and safeguarding the assets of the SM REIT and its schemes.
- This includes ensuring that assets are properly ring-fenced, bank accounts are segregated, and property documents are securely maintained.
ii. Oversight of Investment Manager:
- The trustee ensures that the investment manager adheres to the responsibilities outlined in the regulations.
- They must ensure that the investment manager is not an associate and that they meet the qualifications regarding net worth and experience.
iii. Scheme Management:
- The trustee is responsible for overseeing the activities and operations of the SM REIT’s schemes, ensuring they align with the trust deed’s objectives.
- The trustee must ensure that each scheme’s assets are valued correctly and that real estate assets or properties are properly identified in the scheme offer document.
iv. Regulatory Compliance:
- The trustee ensures that all public communications related to the SM REIT, such as advertisements, blogs, and press releases, comply with the regulations.
- They also oversee meetings of unit holders, especially in issues related to changes in the investment manager, trustee, or any other significant operational changes.
v. Fiduciary Duties:
- The trustee must act in the best interest of the unit holders, ensuring that all actions taken are in accordance with the regulations and the trust deed.
- They are tasked with maintaining transparency, especially in financial matters, by ensuring timely submission of valuation reports and handling unit holder meetings as required by the regulations.
vi. Conflict of Interest Management:
- The trustee must avoid conflicts of interest, particularly with the investment manager, ensuring impartiality in managing the SM REIT’s assets and operations.
- By holding the assets in trust and maintaining oversight over the investment manager, the trustee plays a pivotal role in protecting the interests of the unit holders and ensuring compliance with SEBI regulations.
5. SM REIT Investment Benefits for the Unit Holder/Investor
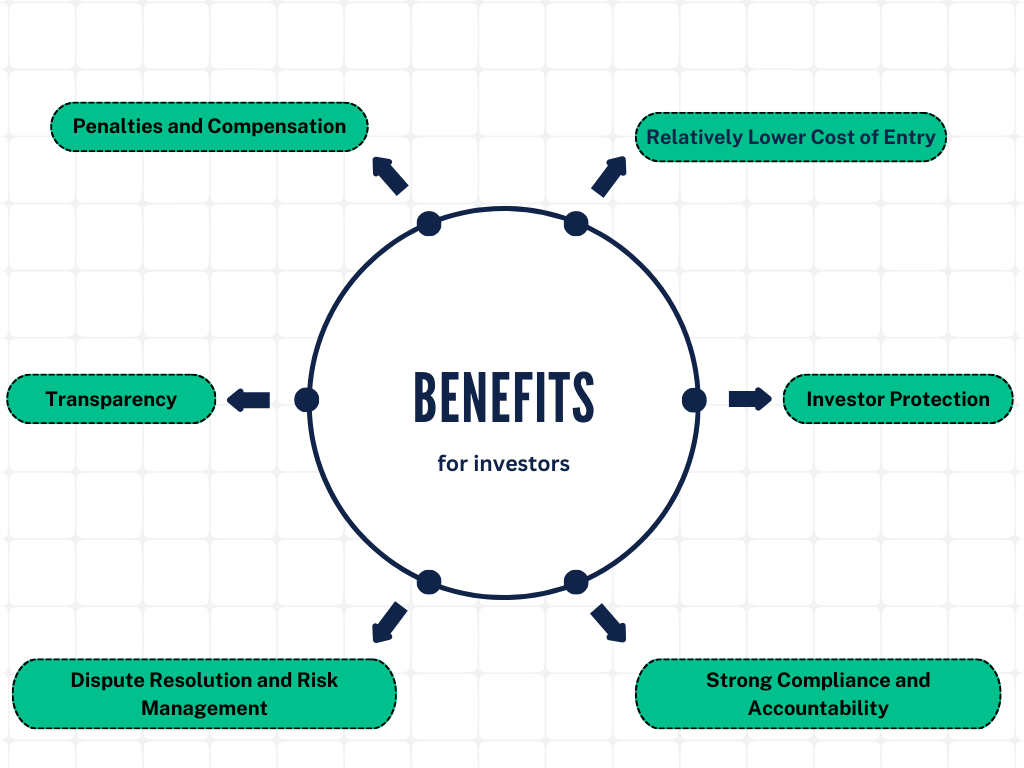
i. Enhanced Transparency
- Public Disclosure of Offer Documents: The investment manager is required to make the draft scheme offer document available for public comment for at least 21 days. This transparency ensures that potential investors have access to essential information before investing.
- Regular Valuation Reports: The investment manager must ensure that comprehensive asset valuations are conducted annually and that these reports are promptly submitted to trustees, stock exchanges, and unitholders. This regular and transparent reporting allows investors to stay informed about the real-time value of their investments.
- Timely Disclosures: The trustee is responsible for ensuring unit holders receive timely and accurate information about the REIT’s performance, financial status, and other significant matters, promoting ongoing transparency.
ii. Investor Protection
- Safeguarding Investor Interests: The trustee holds the assets of the SM REIT in trust, ensuring that they are managed with the highest level of integrity and in the best interests of the unit holders. This fiduciary duty protects investors from potential mismanagement.
- Prohibition on Related Party Transactions: SM REITs are prohibited from entering into related party transactions, with limited exceptions, to prevent conflicts of interest and protect unit holders from unfair dealings.
- Mandatory Distribution of Cash Flows: The investment manager must ensure that 100% of the net distributable cash flows are distributed to unitholders, at least once every quarter. This guarantees that investors receive a regular return on their investment.
iii. Strong Compliance and Accountability
- Obligations of the Investment Manager: The investment manager has several key responsibilities, including maintaining a minimum net worth, ensuring compliance with eligibility criteria, and adhering to strict timelines for unit allotment and listing. Failure to meet these obligations results in penalties, which provide an added layer of protection for investors.
- Trustee’s Oversight: The trustee ensures that the SM REIT complies with all relevant laws and regulations, oversees financial management and property management, and addresses unit holder disputes. This oversight ensures that the REIT operates in a manner that protects the unit holders’ interests.
iv. Dispute Resolution and Risk Management
- Complaint and Dispute Resolution: The trustee is tasked with handling disputes between the REIT, its investment manager, and unit holders, ensuring that investor complaints are managed fairly and transparently.
- Risk Mitigation: The trustee oversees the implementation of risk mitigation strategies to protect the REIT’s assets and the interests of unit holders. This proactive approach to risk management reduces the potential for losses.
v. Legal and Ethical Operations
- Legal Compliance and Ethical Standards: The trustee ensures that all actions taken by the REIT are legally compliant and ethical. They are also responsible for managing conflicts of interest, which further protects the unit holders.
- Governance and Decision-Making: Regular trustee meetings ensure continuous oversight and decision-making on significant issues affecting the REIT, with the primary focus on protecting unit holders’ interests.
vi. Penalties and Compensation
Interest on Delays: If the investment manager fails to meet the deadlines for unit allotment and listing, they must pay 15% interest per annum to the investors. This provision ensures that investors are compensated for any delays and holds the investment manager accountable.
6. Potential Risks in Investing in SM REIT
While regulations definitely offer relief to investors, all investments come with associated risks.
Here are the risks associated with SM REITs investment opportunities:
i. Market Risk: The performance of SM REITs can be affected by fluctuations in the real estate market, including changes in property values, rental income, and overall economic conditions.
ii. Regulatory Risk: Changes in regulations or compliance requirements can impact the operation and profitability of SM REITs. Staying updated with regulatory changes is essential.
iii. Operational Risk: The success of an SM REIT depends on the effective management of its assets. Poor management decisions or operational inefficiencies can affect returns.
iv. Financial Risk: SM REITs often use leverage (debt) to finance their investments. High levels of debt can increase financial risk, especially if income from properties does not meet expectations.
v. Tenant Risk: The income of SM REITs relies on rental income from tenants. High vacancy rates or tenant defaults can reduce revenue and impact overall returns.
vi Property-Specific Risks: Individual properties within the SM REIT portfolio may face specific risks such as maintenance issues, regulatory compliance, or changes in local real estate conditions.
7. Difference between Fractional Ownership and SM REITs
As several prominent fractional ownership platforms transition to the SM REITs structure by obtaining the SM REITs licence, it’s important for investors to recognise the distinctions between these two investment types—fractional ownership and SM REITs.
Although both share core similarities, SM REITs are subject to more comprehensive regulations, providing investors with a more clearly defined and regulated investment option.
| Features | Fractional Ownership (Real Estate) | SM REITs |
| Property Type | Typically preferred for Commercial Real Estate | Both allowed. |
| Investment Approach | Focused approach on a specific property | Focused approach on a specific property |
| Minimum Investor Ticket Size | ₹25 Lacs amongst reputed platforms | ₹10 Lakhs |
| Underlying Assets | Specific property | Specific property |
| Regulations | Companies Act | SM REIT(s) Chapter introduced in the REIT(s) act in March, 2024. Existing Fractional Ownership Platforms (FOP) to migrate here. |
| Offer Size | No such limit. Typically FOPs are offering properties ranging from ₹30-100 Cr | Between ₹50-500 Cr |
| Returns | Fixed rental income plus expected capital appreciation | Fixed rental income plus expected capital appreciation |
| Assets’ Development Requirements | Investments can be made in properties at any stage of development. | SM REITs to invest 95% of their investments in rent-yielding developed properties |
To learn more about fractional ownership and the difference between SM REITs, REITS and fractional ownership, read: Comprehensive Guide To Fractional Ownership
8. Frequently Asked Questions
To understand SM REITs in detail is a herculean task and the government issued an official release of “Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – Framework for Small and Medium REITs” on June 18, 2024.
This SEBI document is a must-read for understanding SM REITs. It provides clear insights into the regulations, market opportunities, and risk management—essential for making informed investment decisions.
Q.1. Can the Investment Manager launch multiple schemes under an SM REIT?
Yes, the REIT Regulations allow the Investment Manager the flexibility to launch multiple schemes under a single SM REIT. However, it’s crucial for both the Investment Manager and the trustee to ensure that each scheme’s assets, bank accounts, investment or demat accounts, and books of accounts are kept separate and protected from each other. This segregation ensures the integrity and security of each scheme within the SM REIT.
Q.2. Which definition of “SPV” (Special purpose Vehicle) is to be considered for the SM REITs regulations?
Since the definition of SPV can be found in two separate places in the REITs regulations (new one being added along with the SM REITs amendment), for the purpose of SM REITs regulations the definition of SPV under section 26H (f) is to be considered.
Definition as per section 26H(f): “Special purpose vehicle” or “SPV” means any company which is a wholly owned subsidiary of the scheme of the SM REIT and the SPV shall not have any other capital or ownership interest in it
Q.3. Can multiple SPVs jointly own a single property?
According to REIT Regulations, an SPV must directly and exclusively own any assets acquired or intended to be acquired by the SM REIT scheme it belongs to. Since an SPV must fully own these assets on its own, multiple SPVs cannot jointly own a single property.
Q.4 Where can you find the official SM REITs regulations?
The official regulations for SM REITs can be accessed through the SEBI website. For detailed information, please refer to the SEBI Real Estate Investment Trusts (Amendment) Regulations, 2024, available at the following link: SEBI Real Estate Investment Trusts (Amendment) Regulations, 2024.
9. Bottom Line
Now that you have a sound understanding of the SM REITs regulations, check out AurumWiseX website to stay updated about upcoming SM REIT scheme launches.